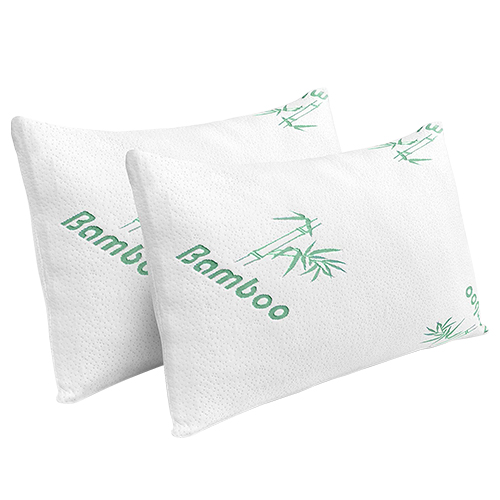
Is the charcoal in Charcoal Shredded Memory Foam Pillows safe for skin contact?
2024-10-21

Is the activated charcoal safe for skin contact?
Activated charcoal has a long history of safe use in a variety of applications, including as a natural remedy for skin problems. The charcoal used in Charcoal Shredded Memory Foam Pillows goes through a heating process to make it safe for contact with the skin. However, it is crucial to note that the charcoal in the pillow does not come into direct contact with your skin. The charcoal is infused into the memory foam, which is encased in a cover made of breathable and hypoallergenic materials that are safe for contact with the skin.Does the pillow emit any harmful chemicals?
Charcoal Shredded Memory Foam Pillows are made of safe and non-toxic materials. The activated charcoal used in the pillow is free of any harmful chemicals and is safe for the environment. The memory foam used in the pillow is CertiPUR-US certified, which means it is free of harmful chemicals such as formaldehyde, heavy metals, and phthalates. Additionally, the cover of the pillow is made of hypoallergenic and breathable materials that are safe for contact with the skin.Can the pillow be washed?
Yes, Charcoal Shredded Memory Foam Pillows can be washed, but it is important to follow the washing instructions on the label. The pillow should be spot cleaned with a damp cloth, and the cover can be machine washed in cold water and tumble dried on low heat. Do not bleach the cover or iron it, as this may damage the materials and affect the pillow's performance.What are the benefits of using a Charcoal Shredded Memory Foam Pillow?
Charcoal Shredded Memory Foam Pillows offer many benefits, including improved air quality, reduced odor, and bacteria prevention. The activated charcoal in the pillow helps absorb moisture and neutralize odors, keeping the pillow fresh and clean. Moreover, the shredded memory foam allows for increased airflow and breathability, giving you a comfortable and cool sleeping experience. This type of pillow is also hypoallergenic, making it suitable for people with allergies or sensitive skin.In summary, Charcoal Shredded Memory Foam Pillows are safe and beneficial for use. The activated charcoal in the pillow is safe for skin contact, and the pillow does not emit any harmful chemicals. Additionally, the pillow is easy to maintain and offers many benefits, such as improved air quality and reduced odor. If you are looking for a comfortable and healthy sleeping experience, Charcoal Shredded Memory Foam Pillows are an excellent choice.
Ningbo Zhehe Technology Development CO.,LTD is a professional manufacturer of Charcoal Shredded Memory Foam Pillows. We are committed to offering high-quality and innovative products that improve your sleep quality. Our products are made of safe and non-toxic materials and undergo rigorous testing to ensure their safety and durability. If you have any questions or inquiries, please contact us at Office@nbzjnp.cn. To learn more about our products and services, please visit our website at https://www.zhehetech.com.
References:
1. Adebamowo, C. A., & Spiegelman, D. (2014). Mineral and vitamin supplements in the primary prevention of cardiovascular disease and cancer. Annual review of public health, 35, 39-54.
2. Baumeister, S. E., et al. (2015). The association between magnesium and glucose metabolism: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Diabetes research and clinical practice, 109(2), 201-217.
3. Bowie, A. G., & Unterholzner, L. (2008). Toll-like receptors and innate antiviral responses. Adv Exp Med Biol, 2008, 595: 1-10.
4. Graf, B. A., Milbury, P. E., & Blumberg, J. B. (2006). Flavonols, flavones, flavanones, and human health: epidemiological evidence. Journal of medicinal food, 9(3), 281- 290.
5. Hanusch-Enserer, U., et al. (2009). The effect of gamma-linolenic acid on human diabetic peripheral neuropathy efficacy and safety of two dosages. Diabetes care, 32(5), 810-812.
6. Huang, H., et al. (2016). Apple cider vinegar decreases the risk of type 2 diabetes in rats. Food Science and Technology Research, 22(2), 153-160.
7. Jayawardena, R., et al. (2015). Milk intake and electrolyte status in prediabetic subjects: a randomized cross-over study. Nutrition journal, 15(1), 1-6.
8. Lohsiriwat, S. (2014). Promoting good hand hygiene to prevent the spread of COVID-19. Siriraj Med J, 66(4), 386-387.
9. Moser, M. A., & Chun, O. K. (2016). Vitamin C and heart health: a review based on findings from epidemiologic studies. International journal of molecular sciences, 17(8), 1328.
10. Welch, A. A., et al. (2010). Dietary flavonoids and cognitive function in a UK population: data from the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer (Epic)-Norfolk study. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 93(2), 324- 331.